In this post, we explain the calibration procedure for DYOR bPED robot.
Assembly of DYOR bPED robot might be misaligned with respect to the home configuration. If the misalignment is not too much, we can use the following calibration procedure so that we can adjust the correct angles by software.
Materials
In this example, we will use DYOR bPED robot (any variant will use the same procedure). In this example, the servos are connected as follows:
- Leg 1 (Right): Pin D4.
- Leg 2 (Left): Pin D5.
- Ankle 1 (Right): Pin D6.
- Ankle 2 (Left): Pin D7.
Facilino
Here we show Facilino’s code to calibrate the robot.
Once the program is uploaded, the robot should be in the home configuration as previously shown. Here we show axis directions (with a “+” sign indicating a positive angle). Legs rotate with a positive angle clockwise (seen from above), while a positive angle rotation on the left foot makes the interior part of the sole to be in contact with the ground and a positive angle rotation on the right foot makes the exterior part of the sole to be in contact with the ground.
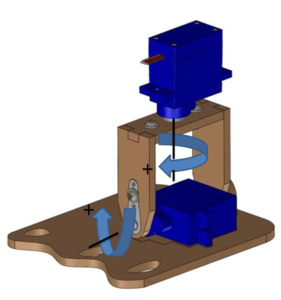
By observing the robot misalignment, we can figure out the correct angle value to adjust, so we need to introduce the opposite value to compensate the misalignment. For instance, if the right leg is rotated clockwise some degrees, we will need to compensate that with a negative value. Repeat this procedure until you have the robot properly calibrated.
What if the calibration values are too high?
In this case, it is convenient to disassemble the robot and make sure that this time the servos are properly positioned at 90º (home configuration). To make sure that the axis does not rotate while we are screwing the servo horns, we can power them, so they will have a torque against being displaced.