In this entry we are going to explain the design and programming of a panda robot based on the proposed DYOR kit.
DESIGN:
The proposed design is based on the DYOR kit from roboticafacil, specifically the panda model. For this purpose, the following components have been used:
- Arduino Nano + Shield Arduino Nano I/O
- Powerbank
- Ultrasound HC-SR04
- Buzzer
- Servos SG90 in the frontal face
- Servos FS90R in the base
- Bluetooth
- Linetracker TCRT5000
- Caster wheel
And the front part has been designed and assembled using SOLID.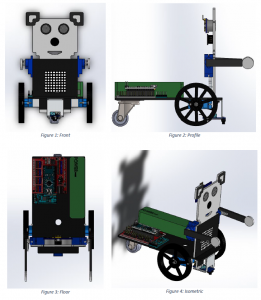
DEVELOPMENT:
Once the robot was configured, I created an Android mobile application, specifically the MIT App Inventor 2 platform. The application sends the information via Bluetooth from the cell phone and is received by the Bluetooth module incorporated in the robot itself.
To create the interface we have used a series of buttons, which depending on which one is pressed has been programmed to send a different signal, and an accelerometer to control the movements of the robot.

The functionalities of each button are as follows:
- The button with the bluetooth image allows you to select the destination bluetooth (the one of the Pandabot) to which you want to transmit the information. The crossed out bluetooth button disconnects the connection.
- The first two buttons starting from the upper left corner, characterized by the image of a happy Panda face and a sad Panda face, draw these expressions on the LED matrix.
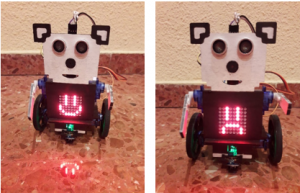
- The panda button with the heart (third button starting from the upper left corner) draws a heart, interspersing a smaller heart with a larger one, on the LED matrix while the song “Love is in the air” is playing.
- The fourth button performs a dance application. When pressed, the song “I want to break free” plays while the Pandabot dances.
- The fifth button shows several “Z” on the LED matrix simulating that the robot is sleeping.
In addition, the robot has two autonomous applications:
- Follow-lines mode: the robot can autonomously follow a black line drawn on the floor. By means of the tctr5000 sensor it detects whether it is on a black line or on a white background, and if it is on the white background, it will move one of the wheels to turn until it is on the black line again.
- Obstacle avoidance mode: the robot turns only when it reaches an obstacle. To do this, the robot will always go in a straight line until it encounters an obstacle with the ultrasonic sensor. When it detects an object, it will turn to avoid it and continue its path in a straight line.
Finally, the remote control has been realized by means of the mobile accelerometer. In this way, when the mobile is tilted forward the robot will move straight forward, when the mobile is turned backwards it will move backwards, when it is turned to the right or left, the robot will turn to one side or the other respectively, and when it becomes horizontal, the robot will stop. In addition, if an object is encountered when remote control is being performed, the robot will stop by emitting a warning noise and drawing a cross on the LED matrix. When it has moved away from the object, the robot will show a happy face on its LED matrix.
CODE:
Finally, all the codes developed for the realization of the robot are attached.
Cristina Asenjo Madrigal
Work done for the Mobile Robotics course.
Master Industrial Engineering – Control, Automation and Robotics.
Universidad Politécnica de Valencia